
Domain Driven Design (DDD)
What is Domain Driven Design and why it is important to define a clear terminology? This article covers the key aspects of developing software following best practices of Domain Driven Design.
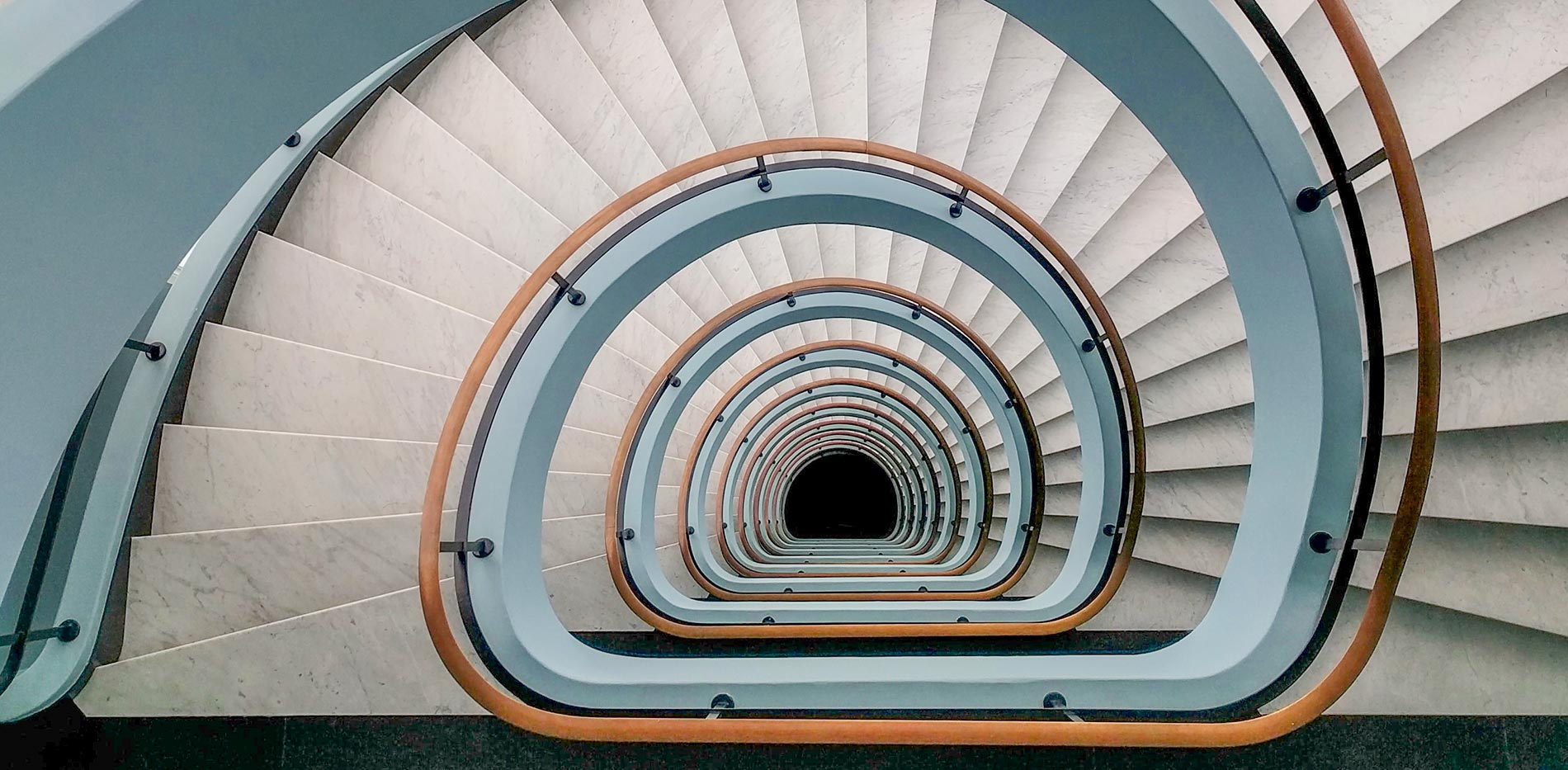


A recursive function is a function designed to call itself directly or indirectly. Using recursion, a problem can be solved by returning the value call of the same particular function.
A recursive function needs to be terminated at some point. The return of a recursive function is usually based on internal conditions which forwards the logic down to a new iteration until the base case is met.
In recursive functions, the base case is that iteration of a recursive function that does not need an additional recursion to solve a problem.
Base cases are mandatory on recursive functions. Without a base case a recursive function will never terminate leading it to an infinite loop.
Sum all values from 0 to given number and display the result.
function sum(number) {
if (number===0) {
return 0;
}
return number + sum(number-1);
}
sum(10);Sum all even numbers from 0 to given number and display the result.
function sumEven(number) {
if (number===0) {
return 0;
} else if (number%2 !== 0) {
return sumEven(number-1);
}
return number + sumEven(number-1);
}
sumEven(10);Returns the value of exponent operation from given number and grade.
function pow(number, power) {
if (power===1) {
return number;
}
return number * pow(number, power-1);
}
pow(2,2);Returns the product of a given number from 1 to N.
function factorial(number) {
if (number===1) {
return 1;
}
return number*factorial(number-1);
}
factorial(3);Display Pascal’s triangular array of the binomial coefficients.
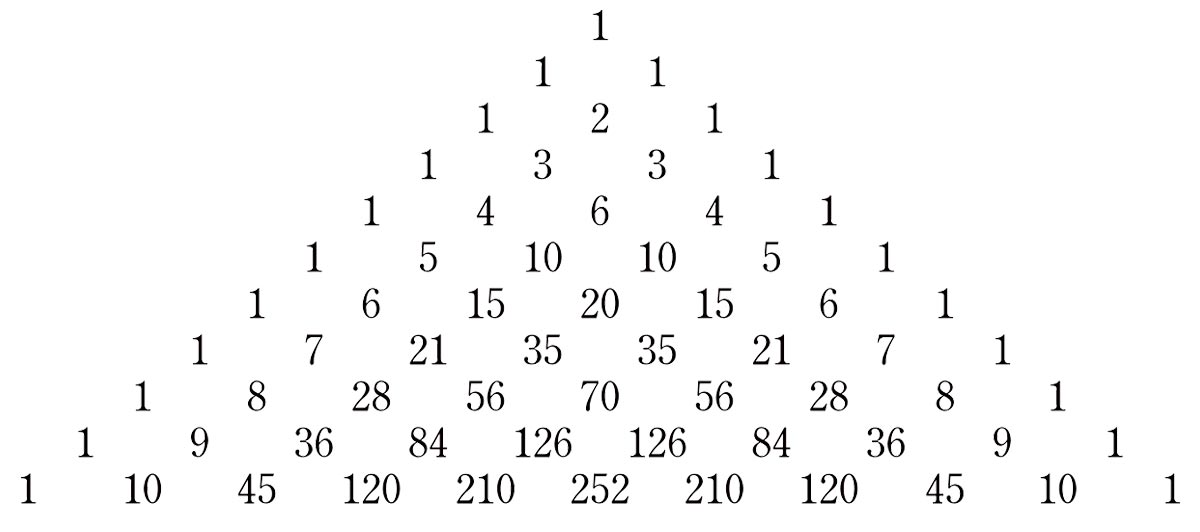
function pascal(row, column) {
if (column>row) {
return 0;
}
if (column<=1 || row<=1) {
return 1;
}
return pascal(row-1, column) + pascal(row-1, column-1);
}
function triangle(number) {
let string = "";
for (let row=1; row<=number; row++) {
for(let column=1; column<=row; column++) {
string += `${pascal(row, column)} `;
}
string += "\n";
}
console.log(string);
}
triangle(10);Displays the Fibonacci sequence from a given number starting with 0.
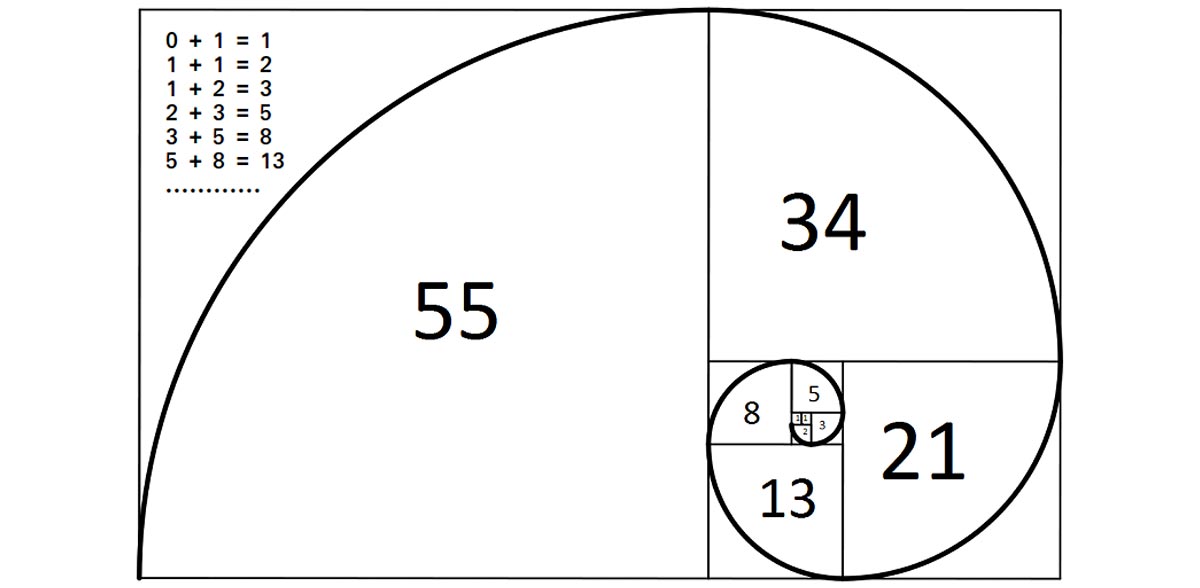
function fib(number) {
function calc(number) {
if (number<=1) {
return number;
}
return calc(number-1) + calc(number-2);
}
let string = '';
for(let i=1; i<=number; i++) {
string += `${calc(i)} `;
}
console.log(string);
}
fib(10)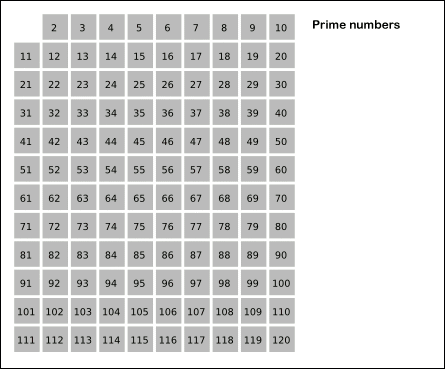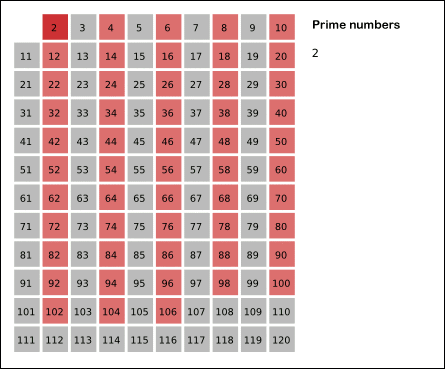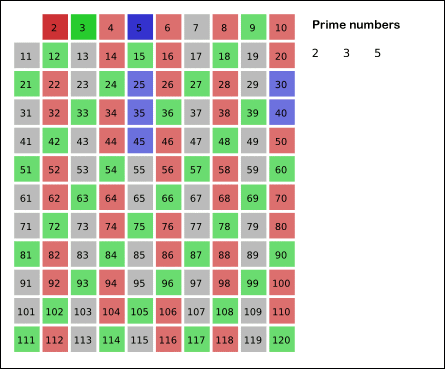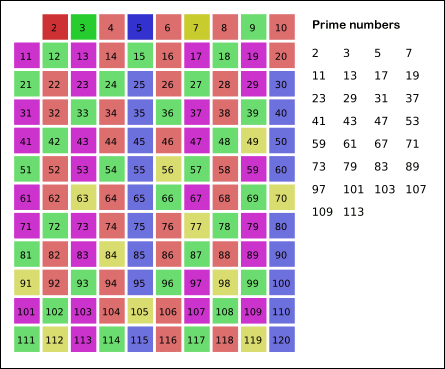
An ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a given number.
function soe(n) {
let a = []
let p = 2
for (let i=p; i<=n; i++) {
a.push(i)
}
console.log(compose(p, a, n).filter(m => m !== 0).join('-'));
}
function compose(p, a, n) {
if (p*p > n) {
return a
}
a = a.map(m => m!==p && m%p===0 ? 0 : m)
p = a.find(m => m!==0 && m>p)
return compose(p, a, n)
}
soe(100);Search a given value on properties of nested objects.
function search(obj, value) {
if (typeof obj !== 'object') {
return obj === value
}
for (const key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key) && search(obj[key], value)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
search({
level_1: {
level_2: {
level_3: {
level_4: {
level_5: {
value: 20
}
}
}
}
}
}, 20);Returns the leaf nodes of a given binary tree.
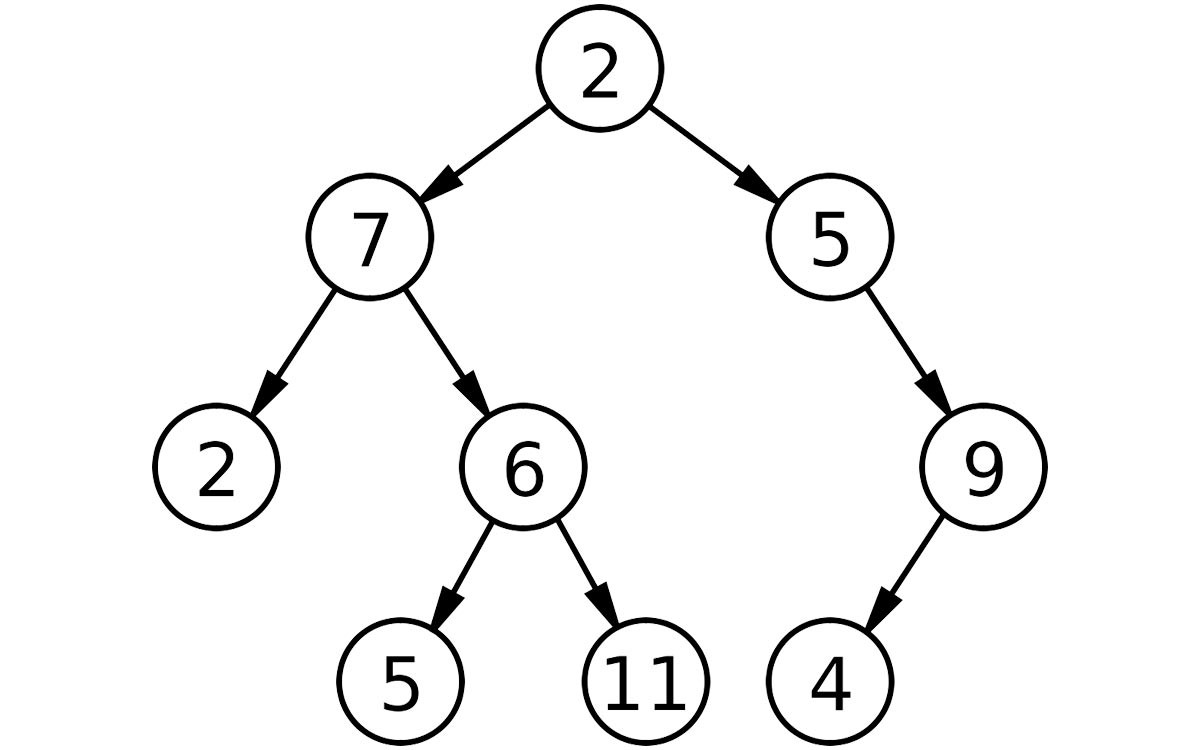
function search_leaf(tree) {
if (!tree.left && !tree.right) {
return tree.value
}
if (tree.left) {
let l = search_leaf(tree.left)
if (l) { console.log(l) }
}
if (tree.right) {
let l = search_leaf(tree.right)
if (l) { console.log(l) }
}
}
search_leaf({
"value": 8,
"left": {
"value": 3,
"left": {
"value": 1,
"left": null,
"right": null
},
"right": {
"value": 6,
"left": {
"value": 4,
"left": null,
"right": null
},
"right": {
"value": 7,
"left": null,
"right": null
}
}
},
"right": {
"value": 10,
"left": null,
"right": {
"value": 14,
"left": {
"value": 13,
"left": null,
"right": null
},
"right": null
}
}
});
Returns the leaf nodes on a Binary Search Tree.
function binary_search_tree(array) {
if (array.length===1) {
console.log(array[0]);
return;
}
const base = array[0]
const right = array.findIndex(n => n>base)
binary_search_tree(array.slice(1,right))
binary_search_tree(array.slice(right))
}
binary_search_tree([890,325,290,530,965]);
What is Domain Driven Design and why it is important to define a clear terminology? This article covers the key aspects of developing software following best practices of Domain Driven Design.

What is code reusability? This article reviews the concepts around code reuse and how to apply them to software development.

PM2 is a process manager for node.js applications. A powerful tool that will facilitate common system administration tasks for node apps.